Damp Prove Course Harmful Effects of DPC Causes of Dampness
Damp prove course, harmful effects of D.P.C, Causes of dampness
what is the damp proof course?
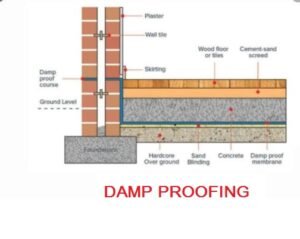
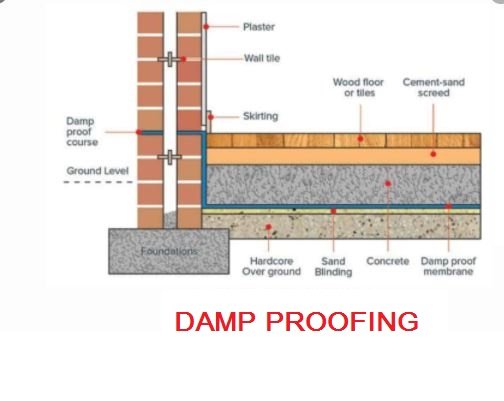
the continuous layer of nonabsorbent materials which is laid between the path of moisture and building structure is called a damp proof course. entrance of any kind of wetness to the building is called should it enters through walls, floors, ceilings, or any other means. this kind of wetness is not only harmful to the building but also to the inhabitants. so it is very essential to detect the cause of wetness as well as the solution for it, so that such buildings may be constructed that is free from dampness.
Harmful effects of DPC
some following harmful effects:
the timber used in the building gets damaged.
the metals used in the building like iron, aluminum, brass, etc get rusty.
plaster bears blistering.
plants get blistering that deteriorates the slape of building.
floors cannot be cleaned properly. so they look ugly.
floor and carpet get rapidly damaged.
Electricity fitting gets damaged.
dampness affects the health of the residents of the building.
Causes of dampness
Learn more
Estimate of the T-wall and what is the T shape wall?
causes of dampness are following is below.
Rains
plinth level of the building
drain ability of the soil
climates
defective orientation
moisture entrapped during construction
moisture originated in the building
Rains
this is the main cause of originating moisture. some buildings can bear heavy rain but for a short period, but rather cannot bear shower continued till many days. finely constructed walls can resist against the entrance of moisture. however, moisture still enters through their purse and joints.
plinth level of the building
plinth level of the building also plays a very important role in either the effects of moisture, decrease or increase. the area slightly above the ground of hear and there would have comparatively lesser effects of moisture.because rainwater would flow around and would not get deposited by the wall of the building.
drain ability of the soil
the ability of the soil is the area where the building stands, to absorb water also plays a very important role of originates moisture or nit, sandy soil drifts moisture by absorbing it but on the other hand, clay does not have this ability but rather, it maintains moisture.
climates
in the cold areas, the dampness of the air gets frozen on the ground. this kind of moisture can normally be seen on the walls as well as ceilings, in the form of the dew of water drop in cold weather.
defective orientation
the walls are consistently hit with rainwater having a defective orientation and do not allow sunlight, In this condition also, moisture orientation.
moisture entrapped during construction
during construction, walls are soaked with water and this moisture can remain for a long time. if salty or saline water has been used in the building for soaking purposes, moisture remains for a long time.
defective material
when porous bricks or soft stone are used particularly in outer surfaces, and saline sand is used, moisture enters the building and gets absorbed.
defective construction
spaces in the joint between the walls and ceiling get left due to recklessness through which rainwater enters the buildings. the window of external walls frames of ventilation windows and specs of the walls also cause moisture.
moisture originated in the building
the deposition of water in some parts of the building for a long time also causes moisture the trickling down of water drops from the pipes of kitchen and bathrooms, the breakage or blockage of sewerage arise the problem of moisture also.
method of prevention dampness
1- damp proof course (DPC)
2- surface treatments
3- integral waterproofing
damp proof course (DPC)
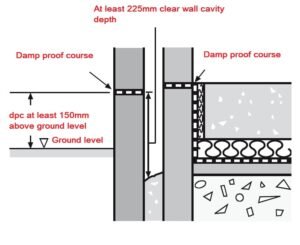
the continuous layer of nonabsorbent materials which is laid between the path of moisture and building structure is called damp proof course. the purpose of this layer is to receive the entrance of moisture into the building, these types of layers are laid in both verticals and horizontal positions, practically, the horizontal layer is laid on external walls, in the entire thickness of the wall at the height of approximately 15cm or 20cm above the ground surface and it is laid on the floor surface in interior walls.
surface treatment
the surface of exterior walls, expose to the air, are painted with water-absorbent paint, but the paints must be durable and water should not get absorbed through the paint. the paint should not harm the beauty of the building.
Integral waterproofing
in this method, such ingredients are included in the mortar or concrete that can properly fill up the pores exit in the building bt their chemical reaction. iron fillings fill up the pore with its chemical reaction. if % of soap is included in the water used for the preparation of mortar, pores are blocked with this morter .thus the elements which does not absorb water gets frozen on the surface of the wall by appearing on the exterior surface of the wall.






Please suggest for dampness treatment best material for wall internal and external.