Difference B/w Flexible and Rigid Pavement
Difference B/w Flexible and Rigid Pavement
Today this article is related to the Difference B/w Flexible pavement and Rigid pavement | Difference B/w Flexible and Rigid Pavement.

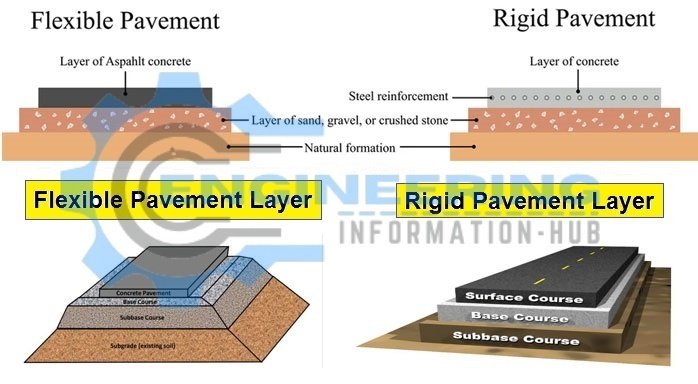
Flexible Pavement
A typical versatile pavement consists of a bituminous surface course over the base course and sub-base course. The surface course might contain one or a lot of bituminous or Hot combined Asphalt (HMA) layers. These pavements have negligible flexure strength and thence endure deformation beneath the action of hundreds. The structural capability of versatile pavements is earned by the combined action of the various layers of the pavement. The load from trucks is directly applied on the carrying course, and it gets distributed (in the shape of a truncated cone) with depth within the base, sub-base, and subgrade courses, and so ultimately to the bottom. Since the strain induced by traffic loading is highest at the highest, the surface layer has the most stiffness (measured by resilient modulus) and contributes the foremost to pavement strength. The layers below have lesser stiffness however are equally necessary within the pavement composition. The subgrade layer is answerable for transferring the load from the top of the layers to the bottom. versatile pavements are designed in such a way that the load that reaches the subgrade doesn’t exceed the bearing capability of the subgrade soil. Consequently, the thicknesses of the layers on top of the subgrade vary relying upon the strength of soil touching the value of a pavement to be created.
Learn More
Transition Curve In Highway -Purpose-Requirements-Example
Bar Bending Schedule For Combined Footing With Four Column
Rigid Pavement
Rigid pavements area unit named therefore due to the high flexural rigidity of the concrete slab and thence the pavement structure deflects little or no below loading because of the high modulus of elasticity of their surface course. The concrete slab is capable of distributing the traffic load into an outsized space with little depth that minimizes the requirement for a variety of layers to assist cut back the strain. the foremost common kind of rigid pavement consists of holdfast bars and tie bars. holdfast bars area unit short steel bars that give a mechanical affiliation between slabs while not proscribing horizontal joint movement. Tie bars on the opposite hand, area unit either malformed steel bars or connectors accustomed hold the faces of connected slabs involved. though they will give some smallest quantity of load transfer, {they area unit|they’re} not designed to act as load transfer devices and are merely accustomed ‘tie’ the 2 concrete slabs along.
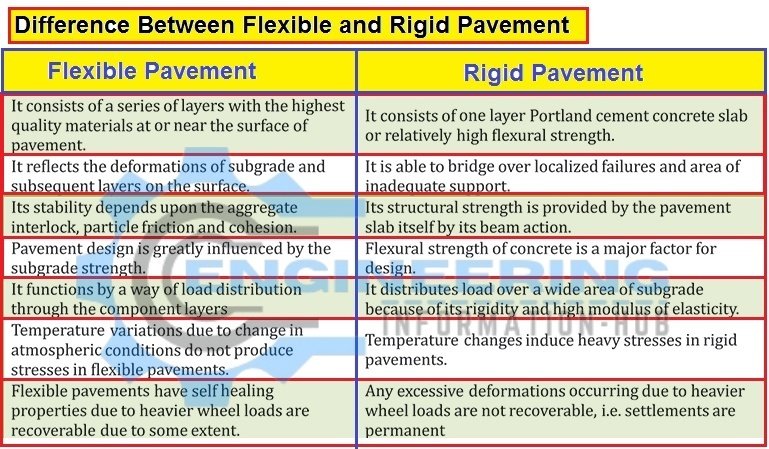
Difference B/w Flexible and Rigid Pavement

Learn More
Elements of The Road & Carriage Method Details
Calculate The Cutting Length Of the Chairs Bar